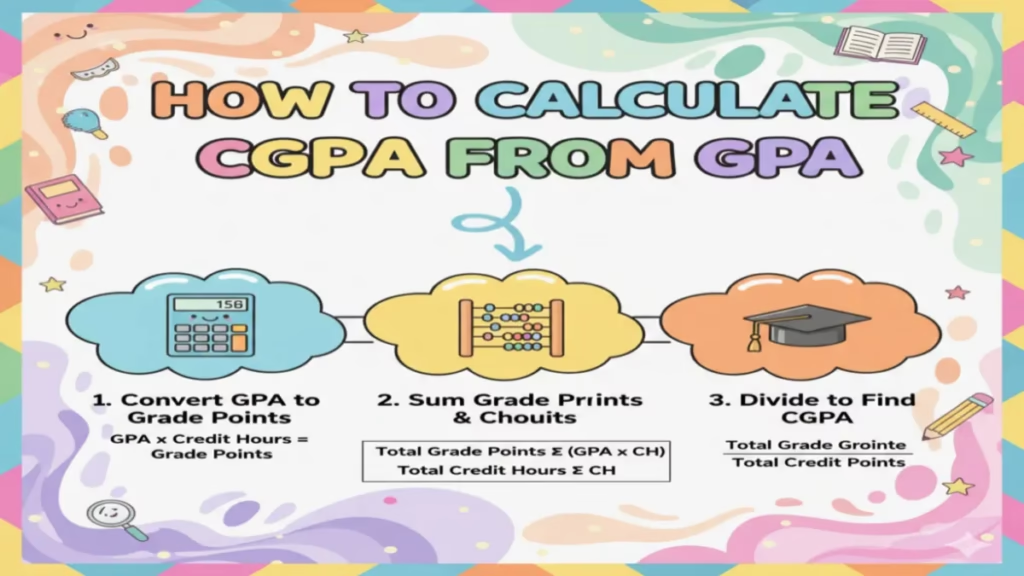
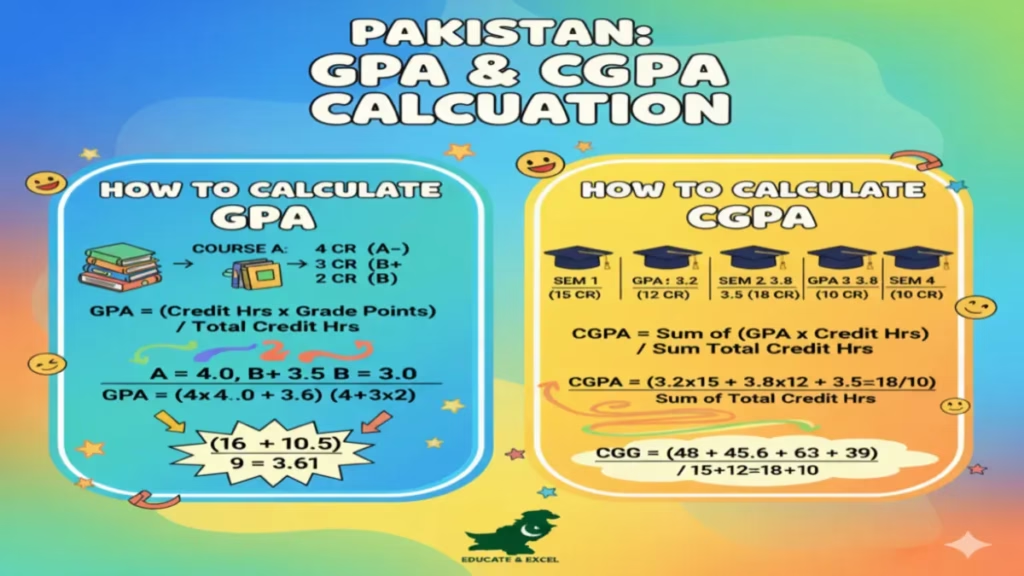
Understanding your grades is a key part of your academic journey. You often hear terms like GPA and CGPA. But what do they mean? More importantly, how do you connect them? Many students wonder how to calculate CGPA from GPA.
This guide will walk you through the entire process. We will break it down into simple, easy-to-follow steps. You will no longer be confused about your cumulative grade point average.
We will use clear examples and plain language. This will help you take control of your academic record. You will be able to calculate your own scores with confidence. Let’s dive into the world of grade calculations and make it simple.
What Is The Difference Between GPA And CGPA?
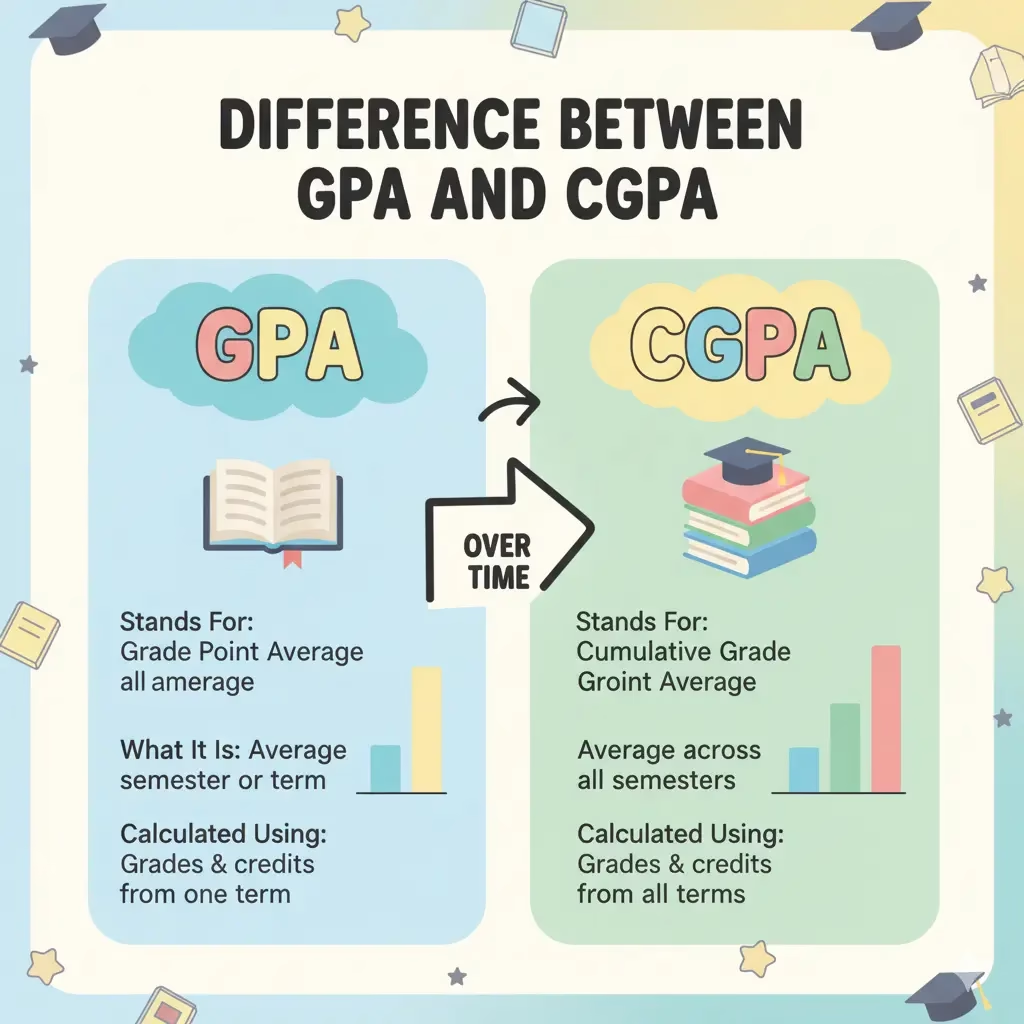
Understanding the difference between GPA (Grade Point Average) and CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) is crucial for every student. While they are related, they measure your academic performance at different scopes and times. Think of it as the difference between a single chapter and the entire book.
GPA: Your Semester-by-Semester Snapshot
GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a measure of your academic performance for a single term. This could be a semester, a trimester, or a quarter.
- What it measures: It calculates the average of the grades you received in all the courses you took during that specific, short period.
- Its scope: It’s a short-term view. It tells you how well you did in a particular set of classes over a few months.
- How it’s used: Your GPA for a semester determines if you make the Dean’s List, if you are in good academic standing for that term, or if you meet the requirements for a scholarship that semester.
In simple terms, your GPA is like your score for one single game in a sports season. It shows how you performed in that specific match but doesn’t define your entire season’s performance.
CGPA: Your Overall Academic Story
CGPA, or Cumulative Grade Point Average, is the comprehensive measure of your performance across your entire academic program. It is the “big picture” of your grades.
- What it measures: It calculates the average of all your grades from all your semesters or years, combined into one single number.
- Its scope: It’s a long-term, cumulative view. It reflects your consistent performance from the day you started your program until the present.
- How it’s used: Your CGPA is often the most important number for your academic career. It is what employers look at on your resume. It determines your eligibility for honors (like cum laude), graduate school applications, and often, your graduation status.
Following the sports analogy, your CGPA is your career batting average or your season-long scoring average. It summarizes your performance across all games, giving a true sense of your overall skill and consistency.

The Key Differences at a Glance
| Feature | GPA (Grade Point Average) | CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average) |
|---|---|---|
| Time Period | Short-term (One semester/term) | Long-term (Entire degree program) |
| Scope | Narrow. Specific to one set of courses. | Broad. Includes all courses from all semesters. |
| Calculation | Based only on the grades from a single term. | Based on the grades from all terms completed so far. |
| Fluctuation | Can change drastically from one semester to the next. | Changes more slowly, as it’s an average of all your work. |
| Primary Use | Monitoring short-term progress and term-specific goals. | Judging overall academic success for degrees, jobs, and honors. |
How They Are Connected: The Calculation
This is the most important practical link between them. Your CGPA is calculated using your GPAs.
You don’t just average the GPA numbers themselves. Instead, you perform a weighted calculation:
- For each semester, you multiply your GPA by the total credit hours for that semester. This gives you your “quality points” for the term.
- You add up all the quality points from every semester.
- You then divide that total by the sum of all the credit hours you have ever attempted.
This method ensures that a semester with more courses (higher credit load) has a greater impact on your overall CGPA than a lighter semester.
Example:
- Semester 1 (15 credits): GPA of 3.5 → 3.5 x 15 = 52.5 quality points
- Semester 2 (18 credits): GPA of 4.0 → 4.0 x 18 = 72 quality points
- Total Quality Points: 52.5 + 72 = 124.5
- Total Credit Hours: 15 + 18 = 33
- Your CGPA: 124.5 / 33 = 3.77
Why Knowing the Difference Matters
Confusing these two terms can lead to misunderstanding your academic standing. You might have a fantastic GPA one semester but still have a lower CGPA if your previous grades were poor. Conversely, a single bad semester’s GPA won’t destroy a strong CGPA you’ve built over years, though it will lower it.
In summary:
- GPA is your grade for a chapter.
- CGPA is the grade for the entire book.
Keeping this distinction clear will help you set better goals, track your progress accurately, and present your academic record correctly to universities and employers.
Why You Can’t Just Average Your GPAs
It seems like the easiest way, right? Just add up all your semester GPAs and divide by the number of semesters. However, this method is almost always incorrect. The reason is credit hours. Not all semesters are created equal. One semester might have 15 credit hours of difficult courses. Another might have a lighter load of 12 credit hours.
A simple average gives equal weight to both. This is not fair. Your 4.0 GPA in a heavy 18-credit semester shows more effort than a 4.0 in a light 12-credit semester. The overall grade point analysis must reflect this.
The correct CGPA computation process is a weighted average. It gives more importance to semesters with more credit hours. This provides a true reflection of your total academic achievement. It is the standard for any college GPA to CGPA conversion.
The Essential Tools You Need Before You Start
Before you begin the calculate final academic score, gather your documents. You will need your official academic transcripts. These documents list your performance for every semester. They are your student academic performance tracker.
From these transcripts, you need two key pieces of information for each semester:
- Your Semester GPA: This is your Grade Point Average for that specific term.
- Your Total Credit Hours: This is the number of credits you were enrolled in that semester.
Make a simple table on a piece of paper. Write down the GPA and credit hours for every semester. Having this data organized is the first and most crucial step in the semester wise grade calculation. It makes the entire process smooth and error-free.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Your CGPA from GPA
Now, let’s get to the main event. Here is a simple, step-by-step final CGPA calculation method. Follow these steps carefully.
Step 1: Collect Your Semester GPAs and Credit Hours
Start by listing all your semesters. For each one, write down two numbers. First, write the GPA you earned that semester. Second, write the total number of credit hours you completed. Let’s use an example. Imagine a student with three semesters:
- Semester 1: GPA = 3.6, Credit Hours = 15
- Semester 2: GPA = 3.8, Credit Hours = 18
- Semester 3: GPA = 3.5, Credit Hours = 12
This is the foundation of your academic record computation.
Step 2: Calculate Your Quality Points for Each Semester
This step is where the weighting happens. For every semester, you will multiply your GPA by the credit hours. The result is called “Quality Points” or “Grade Points.” This figure represents the total value of your performance in that semester, considering its workload.
Using our example:
- Semester 1: 3.6 GPA x 15 Credits = 54 Quality Points
- Semester 2: 3.8 GPA x 18 Credits = 68.4 Quality Points
- Semester 3: 3.5 GPA x 12 Credits = 42 Quality Points
This grade points evaluation formula is the core of an accurate calculation.
Step 3: Find Your Total Cumulative Quality Points
Next, you add up all the Quality Points from every semester. This sum is your total cumulative quality points. It represents the combined weight of all your academic work.
In our example:
54 + 68.4 + 42 = 164.4 Total Cumulative Quality Points.
This number is the top part of your final cumulative average grading system equation.
Step 4: Find Your Total Cumulative Credit Hours
Now, add up all the credit hours from every semester. This is the total number of academic credits you have attempted throughout your program.
In our example:
15 + 18 + 12 = 45 Total Cumulative Credit Hours.
This number will be the bottom part of your final calculation.
Step 5: Divide to Discover Your Final CGPA
This is the final step. Take your Total Cumulative Quality Points (from Step 3) and divide them by your Total Cumulative Credit Hours (from Step 4). The result is your official CGPA.
The semester GPA to CGPA formula is:
CGPA = Total Cumulative Quality Points / Total Cumulative Credit Hours

For our example:
CGPA = 164.4 / 45 = 3.65
Therefore, the student’s final CGPA is 3.65. This academic result percentage converter process is now complete.
Seeing the Calculation in Action: A Detailed Example
Let’s solidify your understanding with a clear example. Imagine Maria, a second-year student. She wants to calculate her CGPA after four semesters. Her academic record is her university result calculation system in a nutshell.
Here is her data:
- Semester 1: GPA = 3.2, Credits = 16
- Semester 2: GPA = 3.7, Credits = 14
- Semester 3: GPA = 3.9, Credits = 18
- Semester 4: GPA = 3.5, Credits = 15
Now, let’s apply the steps.
First, calculate Quality Points for each term:
- Sem 1: 3.2 x 16 = 51.2
- Sem 2: 3.7 x 14 = 51.8
- Sem 3: 3.9 x 18 = 70.2
- Sem 4: 3.5 x 15 = 52.5
Next, find the totals:
- Total Quality Points = 51.2 + 51.8 + 70.2 + 52.5 = 225.7
- Total Credit Hours = 16 + 14 + 18 + 15 = 63
Finally, perform the division:
- CGPA = 225.7 / 63 = 3.58
Maria’s cumulative grade point average is 3.58. Notice that her simple GPA average is (3.2+3.7+3.9+3.5)/4 = 3.58. In this rare case, it matched because her credit hours were similar. But you should always use the weighted method to be accurate. You can use an academic marks percentage calculator that uses this weighted method for convenience.
What is a Grade Conversion Chart?
A grade conversion chart is a simple table or tool. It acts as a bridge between different grading systems. It allows you to take a score from one system and find its equivalent in another. For example, you can see what a “B+” in the US system translates to in a percentage-based system.
Or what a “First Class” degree from India means in terms of a 4.0 GPA. These charts are essential for students applying to international universities. They are also useful for job seekers looking for roles in other countries.
However, it is crucial to remember that these charts are not always official. They provide a general guide. The final decision often rests with the institution receiving your application.
Common Grading Systems Around the World
let’s understand the Common Grading Systems Around the World. Different countries and institutions prefer different methods to evaluate students.
The 4.0 GPA Scale
This is very common in the United States and Canada. Grades are assigned a point value on a 4.0 scale.
- A = 4.0 (Excellent)
- B = 3.0 (Good)
- C = 2.0 (Average)
- D = 1.0 (Pass)
- F = 0.0 (Fail)
Your Grade Point Average (GPA) is the average of these points, weighted by course credit.
The Percentage System
This is a straightforward system used in many countries, including India. Your performance is directly shown as a percentage out of 100.
- 90-100%: Outstanding
- 80-89%: Excellent
- 70-79%: Very Good
- 60-69%: Good
- 50-59%: Satisfactory
- Below 50%: Fail
The CGPA Scale (Often 10-point)
A Cumulative Grade Point Average (CGPA) on a 10-point scale is also widely used. Many institutions in India and Europe use this model.
- 9.0 – 10.0: O (Outstanding)
- 8.0 – 8.9: A+ (Excellent)
- 7.0 – 7.9: A (Very Good)
- 6.0 – 6.9: B+ (Good)
- 5.0 – 5.9: B (Average)
- Below 5.0: F (Fail)
Sample Grade Conversion Chart
The following table provides a general overview of how these different systems might relate to each other. Please use this as a starting point.
| Percentage Range | Letter Grade (US) | 4.0 Scale GPA | 10-Point Scale CGPA | Performance Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 97-100% | A+ | 4.0 | 10.0 | Outstanding |
| 93-96% | A | 4.0 | 9.5 – 9.9 | Excellent |
| 90-92% | A- | 3.7 | 9.0 – 9.4 | Very Good |
| 87-89% | B+ | 3.3 | 8.5 – 8.9 | Good |
| 83-86% | B | 3.0 | 8.0 – 8.4 | Above Average |
| 80-82% | B- | 2.7 | 7.5 – 7.9 | Satisfactory |
| 77-79% | C+ | 2.3 | 7.0 – 7.4 | Average |
| 73-76% | C | 2.0 | 6.5 – 6.9 | Below Average |
| 70-72% | C- | 1.7 | 6.0 – 6.4 | Pass |
| 67-69% | D+ | 1.3 | 5.5 – 5.9 | Poor Pass |
| 65-66% | D | 1.0 | 5.0 – 5.4 | Minimal Pass |
| Below 65% | F | 0.0 | Below 5.0 | Fail |
How to Convert Your Grades Accurately
Using a chart is a great first step. But for official purposes, you need a more precise method. Here are the best practices for accurate grade conversion.
1. The Official Transcript Method
The most reliable method is to check your official transcript. Many modern transcripts already include a conversion table or your calculated CGPA on a 4.0 scale. This is the most trusted source.
2. The WES iGPA Calculator
For students applying to institutions in North America, using the World Education Services (WES) iGPA calculator is a excellent idea. WES is a recognized credential evaluation service. Their tool provides a very reliable estimate of what your grades equate to on a US scale.
3. The Formula-Based Calculation
For a DIY approach, you can use a formula. The most common way to convert a percentage to a 4.0 GPA is not a straight-line conversion. A general formula is:
GPA = (Your Percentage / 20) – 1
However, this is a rough estimate. The exact calculation can vary based on the grading scale your home institution uses.
Important Considerations and Warnings
While conversion charts are helpful, you must be aware of their limitations.
- No Universal Standard: There is no single, globally accepted conversion chart. A 85% in one country or university might be considered a 3.7 GPA, while in another it might be a 3.3.
- Always Check with the Target Institution: The most important rule is to follow the guidelines of the university or employer you are applying to. They may have their own specific conversion table they want you to use.
- Course Rigor is Not Reflected: A conversion chart only translates the grade. It does not account for the difficulty of your courses or the reputation of your school.
Conclusion: Take Control of Your Academic Score
Calculating your CGPA is a powerful skill. It helps you understand where you stand academically. You can track your progress over time. You can set realistic goals for future semesters. The process is straightforward once you know the steps. Remember, it’s all about the weighted average using credit hours. You cannot just take a simple average of your GPAs.
We have covered the complete CGPA computation process. You learned the difference between GPA and CGPA. You saw a step-by-step guide with an example. Now you have the knowledge. Gather your transcripts and calculate your own cumulative grade point average today. Knowing your exact CGPA empowers you. It helps you make informed decisions about your education and future career. You are now your own student academic performance tracker.
Common Questions and Misconceptions
Many students have questions about this process. Let’s clear up a few.
Need a Quick Calculation?
Manually calculating your grades can be time-consuming. To make things easier, I’ve put together a collection of all GPA & CGPA calculators in one place. These tools can help you instantly figure out your scores, so you can spend less time calculating and more time celebrating your success.
👉 Check out all my GPA & CGPA calculators here.